In Situ Stabilization / Solidification (ISS)
In Situ Stabilization / Solidification (ISS) consists of mixing contaminated media with cement and other binding agents. Solidification physically traps the contaminants to form a solid so it has a reduction in porosity and permeability, and has increased durability or strength. Depending on the binding agents used, a degree of stabilization occurs which binds free liquids and immobilizes the chemical constituents.
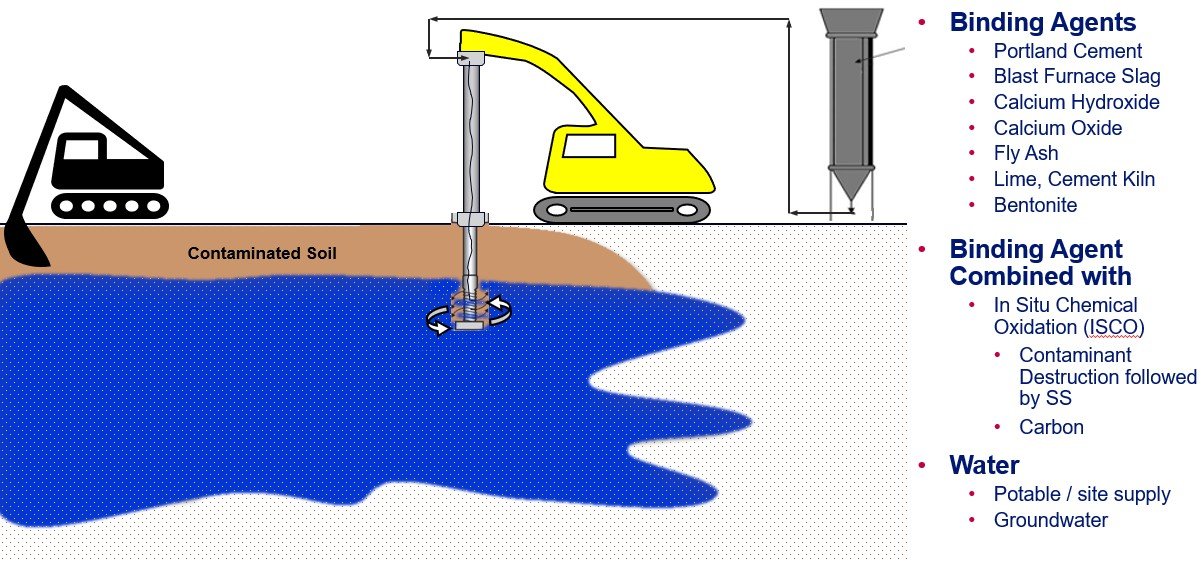
ISS can address a suite of contaminants including volatiles, semi-volatiles, PCBs, pesticides, metals, even PFAS compounds.
ISS can be advantageous when there is a wide range in types and concentrations of contaminants at a site. ISS typically results in increased strength of the treated media at and below the surface, which is important if the site is active or going to be used for future building structures. There is also an associated decrease in permeability and porosity, which minimizes the risk of contaminant migration offsite. Costs are variable, ranging from low to high depending on the reagents used and how they are administered.
Relative to other technologies, ISS is relatively shorter to implement, on the order of a few months.


